Characteristics:
In order to achieve its maximum molding productivities, simply using its ultra micro breathing cell to exhale gas and air from molds.
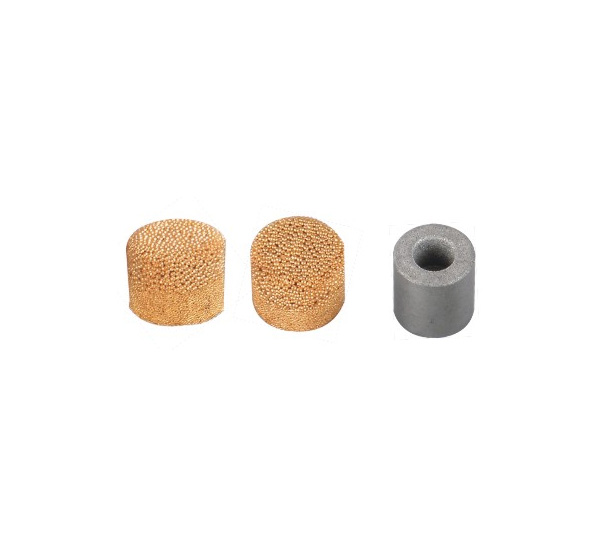
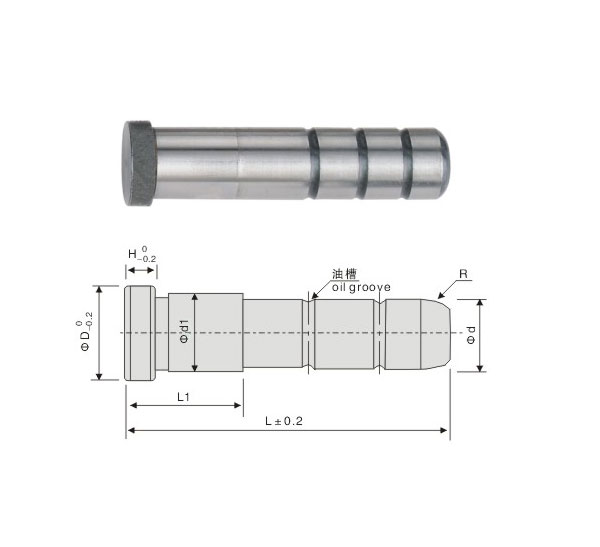
Stainless steel: special for ejection mold Hardness: RV50 pore diameter: 0.03
Copper: special for vacuumed mold Hardness: RV20 pore diameter: 0.5
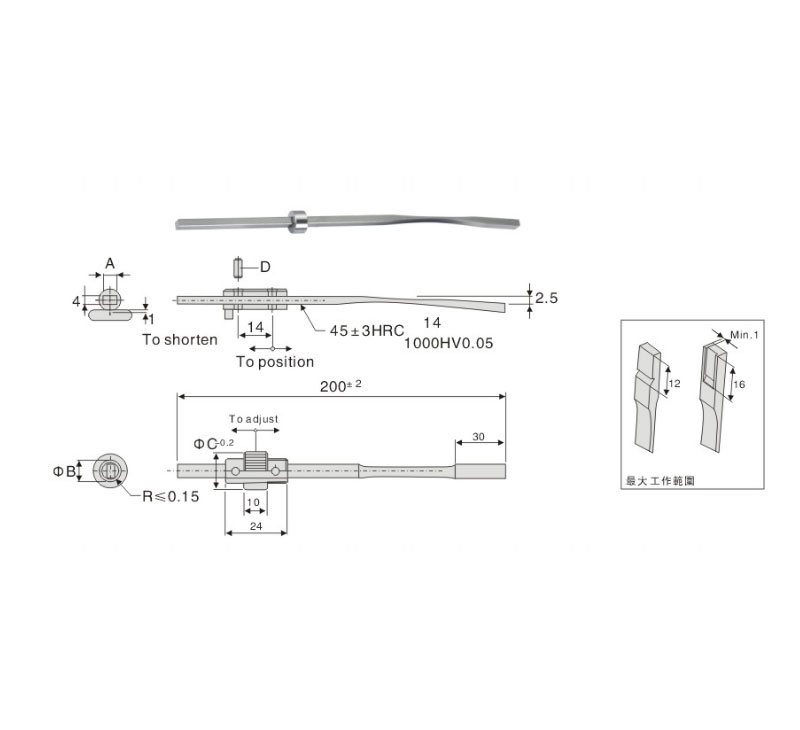
| Catalog No. | L | |
| Type | D | |
| JH077 | 4 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 10 | |
| 6 | 10 | |
| 8 | 10 | |
| 10 | 10 | |
| 12 | 12 | |
• Order: Catalog No. D X L
Common Questions:
1. Burnt
When aberration and burnt issues occurred, it is because resin is filling faster than air exhaling which will result gasvent to overheat.
2. Overflow:
There are 2 possible conditions:
– When temperature of resin gets higher at the tip of seaming, it weakens its bonding strength.
– Air can filled up the path and blocks resin to flow functionally which will cause ejection pressure to rise and materials to overflow.
3. Not enough fillings:
Due to air pressure, it reduces the ratio of the flling speed. Even there is no any sign of burnt or overflow.
4. Cell Streak:
If there are some cells, streaks and mottles occurred, it is because the cells have not been vaporized completely between air and resin.
5. Extensive Cycling Time:
The higher temperature of resin, molds and slower speed of injection cause extensive cycling time, however, it will not affect the
quality of final products.
Energy, Time, and Cost Saver:
1. It will reduce the trial die, time and materials if users consider to use TX gasvent the beginning of the design.
2. It will save up to 1/3 to 1/10 of the total cost and time if installing Sintered Vents.
Installation:
1. Do not touch the surface when Gas Vents is in use.
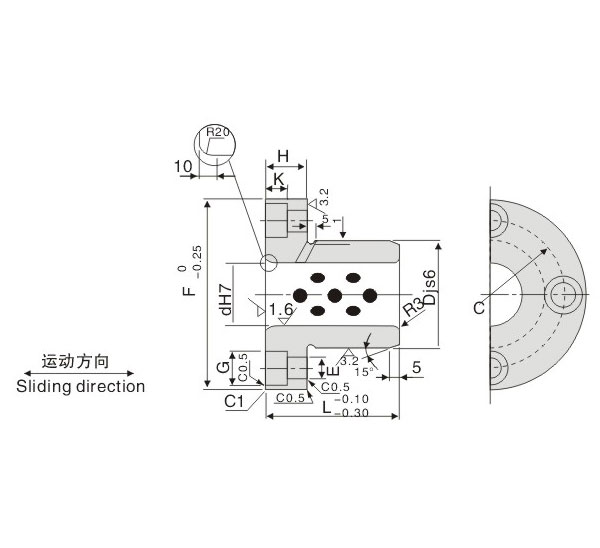
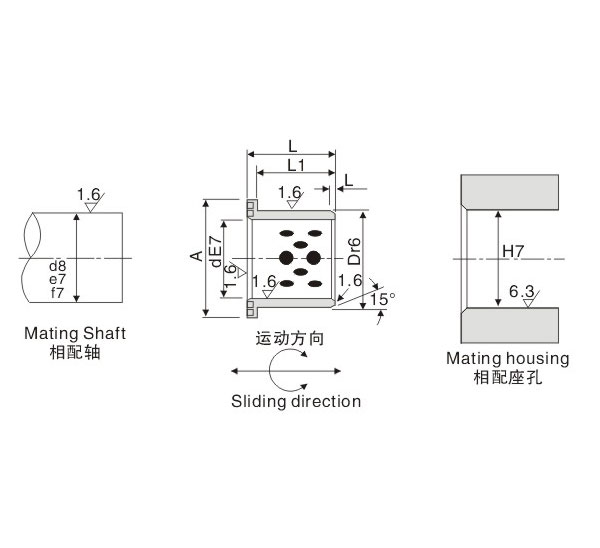
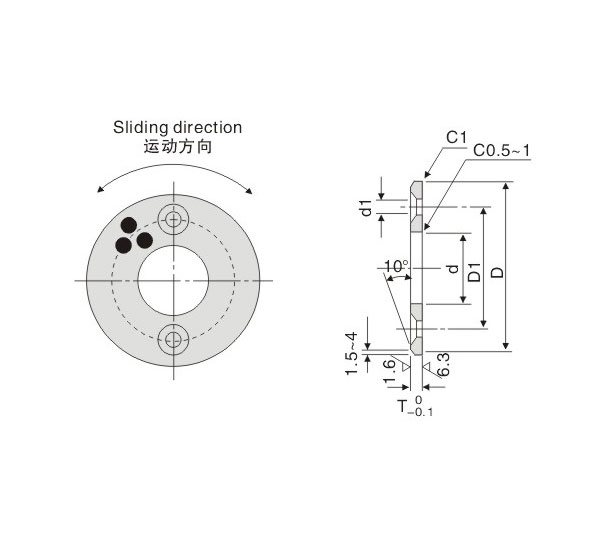
2. Use H7/S6 from JIS reference chart.

 English
English Le français
Le français España
España lingua italiana
lingua italiana